What Is an Economics Glossary?
An economics glossary is a reference tool that defines key terms, concepts, and frameworks used in economic analysis, finance, markets, and policy. It provides clear, concise explanations that help readers understand complex ideas—from supply and demand to financial instruments and macroeconomic indicators. A well-structured glossary supports students, investors, and professionals by making foundational concepts easier to learn, compare, and apply in real-world contexts.

A
Accountability
The obligation of leaders or institutions to answer for their decisions and actions
Acquisition
When one company purchases another by buying either its shares or assets
Administratively Feasible
A policy or program that a government has the capacity, knowledge, and resources to carry out effectively
Adverse Selection
A situation in which private information leads markets to attract participants with hidden risks, often undermining the outcome (such as only unhealthy people buying health insurance)
Aggregate Demand
The total demand for goods and services in an economy at a given overall price level
Aggregate Supply
The total quantity of goods and services that producers in an economy are willing to supply at a given overall price level
Alpha
A measure of an investment’s performance relative to a benchmark, indicating excess return
Allocation
How resources, responsibilities, and benefits are distributed in an economy
Altruism
Taking on a cost to yourself in order to help another person
Antitrust Policy
Laws that prevent monopolies and collusion to keep markets competitive
Arbitrage
The act of buying a good in one market at a low price and selling it in another at a higher price to profit from the difference
Artificially Scarce Good
A good that people can be excluded from using but that one person’s use does not reduce another’s ability to use (such as paywalled digital content)
Asset
Anything of financial value owned, such as property, stocks, or equipment
Asset-Backed Security (ABS)
A financial instrument backed by a pool of loans, such as mortgages or credit card debt
Asset Price Bubble
A rapid increase in the price of an asset driven by speculation and optimism, disconnected from its fundamental value
Asymmetric Information
When one party in a transaction has more or better information than the other
Average Product
Output produced per unit of a particular input, often measured as output per worker
B
Balance Sheet
A financial statement showing assets, liabilities, and net worth
Bank
A financial institution that accepts deposits and issues loans
Bank Money
Deposits created when banks extend loans
Bank Run
A rush of withdrawals by depositors who fear that a bank will collapse
Bargaining Power
The ability to negotiate better terms in a deal or contract
Base Money
Currency in circulation and reserves held by banks at the central bank
Behavioral Experiment
A controlled study designed to observe and measure human decision-making
Best Response
In game theory, the choice that provides the best outcome given the choices of others
Bid-Ask Spread
The difference between the highest price a buyer will pay and the lowest price a seller will accept
Bond Yield
The return an investor earns from holding a bond, usually expressed as a percentage
Budget Constraint
A representation of all possible combinations of goods someone can afford given income and prices
C
Capital Goods
Long-lasting tools and equipment used to produce other goods and services
Capital Structure
The mix of debt and equity a company uses to finance its operations
Capitalism
An economic system in which private owners control firms, hire workers, and sell goods for profit in markets
Capitalist Revolution
The rapid economic growth that began with industrial capitalism, fueled by new technology and market expansion
Cartel
A group of firms colluding to act like a monopoly by fixing prices or limiting output
Causality
A genuine cause-and-effect relationship between two variables
Central Bank
The government institution that issues base money, manages monetary policy, and regulates banks
Ceteris Paribus
Latin for “other things equal,” used to isolate the effect of one factor by holding others constant
Co-Insurance
Sharing resources so that when one household suffers a shock, others provide support
Collateral
An asset pledged to secure a loan, which the lender can seize if the borrower defaults
Commodity
A standardized product, often raw material or agricultural, traded on markets
Common-Pool Resource
A resource that is rival (one person’s use reduces another’s) but hard to exclude people from using (such as fisheries or groundwater)
Competitive Equilibrium
The market outcome where supply equals demand and no participant can unilaterally improve their outcome
Complements
Goods consumed together, where an increase in the price of one reduces demand for the other
Conflict of Interest
A situation where a person’s private interests interfere with professional duties
Conspicuous Consumption
Buying goods or services to display wealth and status
Constant Prices
Prices adjusted for inflation to reflect actual purchasing power
Constant Returns to Scale
When doubling all inputs exactly doubles output
Constrained Choice Problem
A decision-making process where the best option must be chosen within limits like budgets or technology
Consumer Durables
Long-lasting household goods, such as cars or refrigerators
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
An index tracking changes in the average price of consumer goods and services over time
Consumer Surplus
The extra value consumers receive because they are willing to pay more than the actual price
Consumption
Spending on goods and services for personal use
Consumption Smoothing
Efforts to keep consumption stable over time, often through saving or borrowing
Contract
An agreement that defines rights and obligations of parties
Cooperation
Working together for shared benefit
Cooperative Firm
A company owned and run by its workers, who share profits
Copyright
A legal right that gives creators control over the reproduction and use of their work
Correlation
A statistical relationship between two variables, not necessarily causal
Creative Destruction
The process in which innovation replaces old industries with new ones, creating growth while displacing jobs
Credit-Constrained
Facing limits on borrowing or available only at unfavorable terms
Credit-Excluded
Completely unable to borrow
Credit Rationing
When lenders restrict loan amounts, even if borrowers are willing to pay more interest
Crowding Out
When government activity reduces private activity, such as higher spending pushing up interest rates and discouraging private investment
Cyclical Unemployment
Joblessness caused by downturns in overall demand during recessions
D
Debt
Money owed by one party to another
Debt-to-Equity Ratio
A measure that compares how much a company owes to creditors versus how much is financed by shareholders’ investments
Deadweight Loss
The loss of economic efficiency that occurs when markets fail to reach equilibrium, such as from taxes or price controls
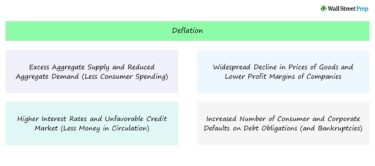
Deflation
A sustained decrease in the overall price level
Demand Curve
A graph showing the quantity of a good consumers are willing to buy at different prices
Derivative
A financial contract with a value that depends on an underlying asset, such as options, futures, or swaps
Diminishing Returns
The principle that adding more of one input while holding others constant eventually produces smaller increases in output
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF)
A valuation method that estimates a company’s value by projecting future cash flows and discounting them to present value
Discount Rate
The interest rate used to determine the present value of future payments
Disposable Income
Income available to spend or save after taxes and transfers
E
Equity Financing
Raising capital by selling shares of stock
Equilibrium
A state where opposing forces are balanced, such as supply equaling demand
Equity
Ownership in a company, or fairness in resource distribution
Externality
A cost or benefit of an action that affects others who did not choose it
F
Fiscal Policy
Government decisions on spending and taxation to influence the economy
Free Rider
Someone who benefits from a resource or service without paying for it
Frictional Unemployment
Short-term unemployment occurring as people change jobs
G
Game Theory
The study of strategic decision-making among interdependent participants
GDP (Gross Domestic Product)
The total value of goods and services produced within a country over a period
H
Hedging
Using financial instruments to reduce the risk of adverse price movements
Human Capital
The skills, knowledge, and experience possessed by individuals
Hyperinflation
Extremely high and accelerating inflation that erodes currency value
I
Imperfect Competition
Market conditions where individual firms have some control over prices
Inflation
A general increase in prices over time
Initial Public Offering (IPO)
The first sale of a company’s shares to the public
Interest Rate
The cost of borrowing money or return for lending
Investment
Spending on assets that will generate future returns
L
Labor Force
The total number of people employed or actively seeking employment
Leveraged Buyout (LBO)
Acquisition of a company using a high proportion of borrowed funds
Liquidity
The ease of converting an asset into cash without significant loss of value
Liquidity Risk
The risk of being unable to sell an asset quickly without losing value
M
Marginal Cost
The extra cost of producing one additional unit of output
Marginal Product
Additional output produced by one more unit of input
Market Capitalization
The total value of a company’s shares (price per share times number of shares)
Market Failure
When markets fail to allocate resources efficiently
Market Power
The ability of a firm to set prices above competitive levels
Merger
The combination of two companies into one
Monetary Policy
Actions by a central bank to control money supply and interest rates
Monopoly
A market with only one seller
Moral Hazard
When one party takes greater risks because they do not bear the full consequences
N
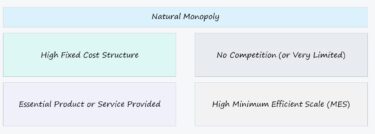
Natural Monopoly
A market where a single firm can supply the entire market at lower cost than multiple firms
Nominal Value
The stated value of money or prices, unadjusted for inflation
O
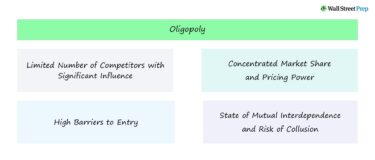
Oligopoly
A market dominated by a few firms
Opportunity Cost
The value of the next best alternative forgone
Option
A contract giving the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a set price before a specific date
P
Principal-Agent Problem
A situation where an agent’s interests differ from the principal’s, creating potential conflicts
Private Equity
Investments in privately held companies, often with active management and eventual exit
Productivity
Output per unit of input
Property Rights
Legal rights over the use and transfer of resources
Public Good
A non-rival, non-excludable good, such as national defense
Q
Quota
A limit on the production or import of a good
R
Real Wage
Wages adjusted for inflation
Recession
A period of declining economic activity
Rent-seeking
Seeking wealth without creating value, often through manipulation or lobbying
Return on Equity (ROE)
Profitability relative to shareholders’ equity
S
Scarcity
The fundamental economic problem of limited resources and unlimited wants
Securities
Tradable financial assets like stocks, bonds, or derivatives
Shareholder
An owner of shares in a company
Spread
The difference between yields, interest rates, or bid and ask prices
Structural Unemployment
Long-term unemployment caused by shifts in the economy
Substitute Goods
Goods that can replace each other in consumption
Supply Curve
A graph showing the quantity supplied at different prices
T
Tangible Asset
A physical resource that has a finite monetary value
Tax Incidence
The distribution of the economic burden of a tax
Technological Change
Advances that improve production methods
Trade-Off
A choice requiring giving up one thing for another
U
Underwriting
The process by which investment banks evaluate and assume the risk of issuing new securities
Unemployment Rate
The percentage of the labor force actively seeking work but unable to find it
Utility
Satisfaction or happiness from consuming goods and services
V
Valuation Multiples
Ratios used to value companies, such as P/E or EV/EBITDA
Venture Capital
Investment in early-stage companies with high growth potential
Volatility
The degree of variation in an asset’s price over time
W
Wage
Payment to workers for labor
Wealth
Total value of what someone owns minus debts
Y
Yield Curve
A graph of interest rates for bonds with different maturities
Z
Zero-Sum Game
A situation in which one participant’s gain equals another’s loss
Additional Resources
- What Is Economics?
- The A to Z of Economics
- Types of Investment Products
- Investing in Green Bonds
- Recession, Hyperinflation, and Stagflation
- Understanding Private Equity Funds
- Private Equity Analyst Training
- How Financial Markets Work
- Real Estate Financial Modeling
- Guide to Value Investing
- Valuation Modeling Certification
- Fiscal Policy: Taking and Giving Away